1. About Lightning
2. Lightning hazards
3. Precautions against Lightning
1. About Lightning
Lightning is a natural disaster and it causes death and damage all over the globe. It continues to be a frequent killer.
Lightning is responsible for a considerable number of deaths in Sri Lanka every year. Information collected via media and personnel contacts witnesses 49 deaths of human beings and 16 deaths of animals during 1997. Since there may be many more cases with no information going to any communication media, the actual figures are obviously more than the above-mentioned values. Number of injured people in lightning incidents may be over 50 every year.
Damage to property and loss of life by lightning flashes are on the increase with the increase of population and the use of modern electrical and electronic equipment in our day-to-day lives. Houses and other buildings are constructed in all environments. Increased exposure of buildings to the atmosphere and improper planning in construction are some of the factors that enhance lightning hazards to buildings. A considerable damage to buildings by lightning is reported every year in Sri Lanka. Some buildings are partly or completely destroyed and some catch fire.
Life loss in lightning incidents is mainly due to the fact that precautionary steps are not being taken to reduce or avoid lightning hazards. Lightning affects people indoors of outdoors. The location, physical properties of buildings may be favorable for increased attraction of lightning flashes leading to damages. Some of the deaths and the damage could have been avoided had precautions been taken in the stages of planning and construction. Therefore, precautionary steps have to be taken during all the construction stages of all buildings in order to reduce and mitigate damages by lightning to the buildings and inhabitants.
The weather experienced during a 12 month period in Sri Lanka can be categorized into four (4) seasons as follow.
i. First Inter Monsoon season March - April
ii. South West Monsoon season May - September
iii. Second Inter Monsoon season October- November
iv. North East Monsoon season December - February
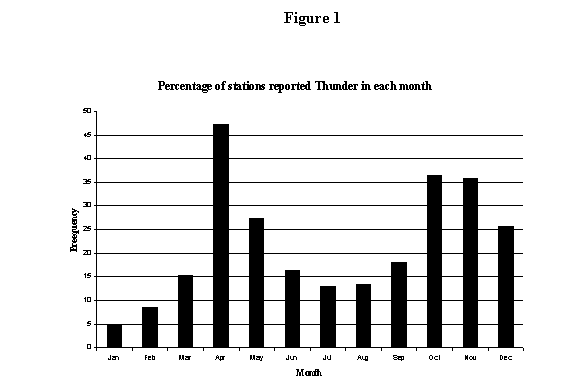
Lightning activity over Sri Lanka shows peaks during the two Inter-monsoon seasons of March-April and October-November (Figure 1). During these periods convective clouds develop over most parts of the island, mostly during the afternoon or evening. The well-developed convective clouds which produces thunderstorms are technically called 'Cumulonimbus'. Since thunderstorms develop under any atmospheric conditions that are capable of developing convective clouds, we should be alert in launching precautionary steps to reduce lightning hazards during all seasons.
Static electric charges in cumulonimbus clouds and lightning
A well developed cumulonimbus cloud is electrically charged and the static charges are distributed in the cloud so that the negative charges are concentrated in the lower part of the cloud and positive charges over the upper part. Under the influence of a charged cloud the earth surface is positively charged by induction.
Lightning is merely electrical discharges associated with the charged cumulonimbus clouds. Depending on the way of discharging they are grouped into three main types.
(a) Cloud to ground Flash (Ground Flash); Discharge between clouds and the earth
(b) Cloud Flash (intra cloud flash): Discharge within a cloud
(c) Air Flash: Discharge between clouds and the atmosphere
The ground flash, which is important as a hazardous event, is the electrical discharge between the negative charge center of a cloud and the positive charge center on the ground. Under certain conditions, positive ground flashes may occur between the positive charge center of a cloud and the earth.
Characteristics of lightning
The electric current of a ground lightning flash is about 25000 Amperes (25000 A) and the potential difference between a charged cloud and the earth is about 100 million Volts. Therefore the energy of a lightning flash bringing 5 coulombs to ground is about 500 million Joules.
Types of lightning strikes During weather conditions with thunderstorms, lightning surges may reach an object or the inside of a building in a number of ways.
Direct hit
It is obvious that lonely (considerably tall) buildings are vulnerable to lightning flashes. Once it strikes a building the lightning current will pass through the conductive materials of the building (reinforcing steel in concrete columns and slabs, wiring, electrical circuits, metal structures etc.) on its way to the ground if there is no safe way provided for the purpose. Selection of the path is decided by a number of factors like specific resistance and the situation etc. of the conducting parts or elements within the building.
Side Flash
A part or the whole current of a lightning flash which has hit a close by telephone, power line or a TV antenna may travel to a building via the electrical (metal) connection between the point of strike and the building. Also, depending on a number of parameters, part of a lightning flash that has reached a close by tall object (tree or tower) may spark to the conducting parts (concrete sun shade, concrete chimney, roof or aluminum sheet) of a building even without any electrical connection.
Inductively by electric and magnetic field coupling.
When a lightning current passes through air or a conductor it first rises to a maximum, which is about 25000 A and then falls to zero, both changes taking place in a short period (about 10 and 80 micro seconds respectively). Change of an electric current induces an electric motive force (or a potential difference) between two ends of any conductor in the vicinity. This is called induction.
2. Lightning hazards
Lightning is responsible for a considerable number of deaths and damage that occurred during the first inter monsoon season in 2002. A death toll of 37 people and damage to three houses by fire, all caused by lightning, were included in the list of the natural hazards reported in the media during March-April 2002. The actual death toll and the damages may be much higher as the information of all hazards by lightning, like other hazards, is not reported to the media
Like rainfall, lightning activity in an area is significantly variable with the time of the day and the season of the year. Therefore one cannot expect the activity, strength and intensity of thunderstorms to have similar characteristics all the time and every year. Development of thunderclouds, frequency and intensity of lightning etc. depend on a number of meteorological parameters and geographical parameters of a location.
Besides all these, lightning is a natural event and it should occur for the sake of maintaining the electrical balance of the earth. The proposals of some people to catch and store the enormous energy of the lightning flashes for useful purposes are encouraging. But practically it is not an easy task to collect the energy of a lightning flash and, on the other hand, if we do so it will definitely affect the electrical balance of the globe (including the atmosphere). For these reasons, we should take all necessary precautionary steps to avoid or at least minimize the hazards caused by deadly lightning.
3. Precautions against Lightning
A lightning flash, after traveling a distance about half a kilometer from clouds selects a closest conducting path to approach the earth before getting neutralized. Therefore, the tallest objects in a location are the best callers or supporters for a lightning flash on its way to the ground. In a natural environment, tall trees are the lightning-attracters. Otherwise conducting (metal) structures or objects (like communication towers, telephone and power supply lines and TV antenna) will attract the close by lightning flashes. In absence of such objects, the buildings in the location are vulnerable to direct hit of thunderbolts.
Life and Property
Lightning flash is a quick discharge of extraordinary electric energy and it can cause damage to any object through which it flows towards the earth. Such a flash can cause loss of life and physical damage to human beings, animal and property.
As mentioned earlier, lightning is a natural phenomenon and therefore it is difficult to stop it. But the hazards caused by lightning could be reduced with a number of precautionary measures.
It has been noticed that a number of lives are lost in thunderstorms mainly due to the negative response of the people in launching precautionary steps that could be taken in order to reduce hazards.
Lightning damages are resulted in different ways.
a. Direct hit -
Lightning flash descending from a cloud hits an object directly.
b. Contact potential -
Shock occurs when there is contact with an object like a tree, building or a
conducting wire those acts as a part of a conductor of a lightning current.
c. Side flash -
Shock occurs when one is close to an object like a tree, building or a
conducting wire those acts as a part of a conductor of a lightning current.
d. Step voltage -
Voltage difference between feet resulted by a current spreading from a
point of a lightning strike on the ground .
It is beyond our control to stop lightning. But carefulness in launching precautionary steps may reduce the hazards.
A few precautionary steps to be considered in order to reduce lightning hazards are mentioned below.
A.
Do not have any conducting connection (like wires) between houses and the close-by trees. The cloth-line wire and the wire used as supports to old and weak trees are two hazardous examples.
B.
Different kinds of conducting materials existing in the environment help in conducting the huge current of a lightning stroke, partly or fully, from place to place. Electric power supply cables, telephone cables and TV antenna cables are good examples. Therefore, in environments with thunderstorms,
(i). Keep electrical instruments disconnected from the main power supply.
(ii). Television antennas should be disconnected from the television sets and the antenna socket should be placed close to the earth outside the house. Best precaution is connecting the antenna to an earthed conductor.
(iii). As far as possible, avoid handling/touching electrical instruments like refrigerator, electric iron, metal frame, TV, and radio.
(iv). Avoid touching or standing close to tall metal structures, wire fences and metal clothes lines.
(v). Limit the use of telephones when a thunderstorm is overhead. Best advice is not to touch the telephone in such instances.
C.
Find shelter in a safe place to avoid exposing yourself to the open air. If the time interval between lightning flash and hearing thunder becomes less than 15 seconds, move quickly to a protected location, as there is immediate danger of a lightning strike nearby.
D.
in environments with thunderstorms
(i). Try to avoid loitering in open areas like paddy fields, tea estates or play grounds. Specially avoid working in open air holding metal tools like mammoty, knife and iron rods. If this cannot be avoided, crouch down, singly, with feet together. Footwear or a layer of any non-absorbing material, such as plastic sheet, will offer some protection against ground currents.
(ii). Do not seek shelter under or near isolated tall trees and in high grounds. If the vicinity of a tree cannot be avoided, seek a position just beyond the spread of the foliage.
(iii). By sitting down or lying down, reduce the effective height of the body
(iv). If in an open boat, keep a low profile. Additional protection is gained by anchoring under relatively high objects such as jetties and bridges, provided that no direct contact is made with them.
(v) Avoid riding horses or bicycles, or riding in any open vehicle such as a tractor.
(vi). Avoid swimming or wading.
Life of a thundercloud is short as 30 minutes. As a result, fatal lightning occurs during a very short period like 10-20 minutes. If we are careful to take necessary precautionary steps during that period it is obvious that the lightning hazards can be reduced. It should be stressed that the first lightning flash and the flash following a short break of activity cause most of severe damage to life.
First aid
Lightning hazards are not fatal always. The state of the damage depends on the path of the lighting discharge through the body and the intensity of the current. In case of lighting strikes to persons, first aid should be given to the diseased before taking him for medical treatments.
Body should be massaged to treat in case of temporary paralysis due to lightning strikes. If respiration is disturbed, artificial respiration should be tried. This could be done by blowing air into the patients body through his mouth. In many cases, massage and artificial respiration have to be given simultaneously.
*There is no danger in touching, holding or carrying a person struck by lightning.
Please direct any information or inquiries about lightning incidents and precautionary measures to Director, Department of Meteorology, Colombo 7